- Offensive Security Training: Developers of Kali Linux and Exploit DB, and the creators of the Metasploit Unleashed and Penetration Testing with Kali Linux course.
- DEFCON: Information about the largest annual hacker convention in the US, including past speeches, video, archives, and updates on the next upcoming show as well as links and other details.
- Phrack Magazine: Digital hacking magazine.
- SecTools.Org: List of 75 security tools based on a 2003 vote by hackers.
- HackRead: HackRead is a News Platform that centers on InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News with full-scale reviews on Social Media Platforms.
- Metasploit: Find security issues, verify vulnerability mitigations & manage security assessments with Metasploit. Get the worlds best penetration testing software now.
- Exploit DB: An archive of exploits and vulnerable software by Offensive Security. The site collects exploits from submissions and mailing lists and concentrates them in a single database.
- Makezine: Magazine that celebrates your right to tweak, hack, and bend any technology to your own will.
- Hack Forums: Emphasis on white hat, with categories for hacking, coding and computer security.
- Hacked Gadgets: A resource for DIY project documentation as well as general gadget and technology news.
- KitPloit: Leading source of Security Tools, Hacking Tools, CyberSecurity and Network Security.
- SecurityFocus: Provides security information to all members of the security community, from end users, security hobbyists and network administrators to security consultants, IT Managers, CIOs and CSOs.
- Packet Storm: Information Security Services, News, Files, Tools, Exploits, Advisories and Whitepapers.
- Black Hat: The Black Hat Briefings have become the biggest and the most important security conference series in the world by sticking to our core value: serving the information security community by delivering timely, actionable security information in a friendly, vendor-neutral environment.
- Hackaday: A hardware hack every day.
- NFOHump: Offers up-to-date .NFO files and reviews on the latest pirate software releases.
- The Hacker News: The Hacker News — most trusted and widely-acknowledged online cyber security news magazine with in-depth technical coverage for cybersecurity.
- Hakin9: E-magazine offering in-depth looks at both attack and defense techniques and concentrates on difficult technical issues.
Tuesday, June 30, 2020
Ethical hacking : Top 18 best websites to learn hacking 2018
Friday, June 12, 2020
Remot3d - An Easy Way To Exploiting
Related word
Thursday, June 11, 2020
How To Secure Your Home Against "Internet Of Things" And FUD
TL;DR, most of the security news about IoT is full of FUD. Always put the risks in context - who can exploit this and what can the attacker do with it. Most story only covers the latter.
Introduction
There is rarely a day without news that another "Internet of Things" got hacked. "Smart" safes, "smart" rifles, "smart" cars, "smart" fridges, "smart" TVs, "smart" alarm systems, "smart" meters, "smart" bulbs, NAS devices, routers. These devices are getting hacked every day. Because most of these devices were never designed with security as a goal, and some of them have been never tested by security professionals, it is no surprise that these things are full of vulnerabilities.
Independent security researchers find these vulnerabilities, write a cool blog post or give a presentation about the vulnerability and the exploit, and the media forgets the constraints just for the sake of more clicks. "We are all doomed" we can read in the news, but sometimes the risks are buried deeply in technical jargon. Please note I blame the news sites here, not the researchers.
 |
| http://www.slideshare.net/danielmiessler/iot-attack-surfaces-defcon-2015 |
There are huge differences between the following risks:
- Attackers can directly communicate with the router (or camera) from the Internet without authentication and exploit the vulnerability. This is the worst-case scenario. For example, an automated ransomware attack against your NAS is pretty bad.
- Attackers have to position themselves in the same WAN network (e.g. Sprint mobile network in the case of Jeep hacking) to exploit the vulnerability. This is still pretty bad.
- The vulnerable code can not be triggered directly from the Internet, but tricks like CSRF can be used to exploit it (details later in this post).
- The vulnerable code can not be triggered directly from the Internet, and it uses a protocol/port which prevents Cross Protocol Scripting. Attackers have to access the local network before exploiting this vulnerability.
As it is the case with the worst scenario, one can find a lot of devices connected to the internet. You can always find funny stuff at http://explorer.shodanhq.com/#/explore , or use the nmap screenshot script to find your own stuff :)
Network exposure
Most devices are behind an IPv4 NAT device (e.g. home router), thus can not be reached from the Internet side by default. Except when the device configures the firewall via UPNP. Or the device has a persistence cloud connection, and the cloud can send commands to the device. Or the device uses IPv6 tunneling (e.g. Teredo), thus it is reachable from the Internet. But not every vulnerability on your home network is accessible directly from the Internet. As more and more devices and networks will support IPv6, this scenario might change, but I hope most home routers will come with a default deny configuration in their IPv6 firewall module. On the other hand, scanning for IPv6 devices blindly is not feasible due to the large number of IPv6 addresses, but some tricks might work.
If attackers can not access the device directly, there is a way to hack it through the user's browser. Just convince the victim user to visit a website, and via CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery) and brute-forcing the device IP, it is possible to hack some devices (mostly through HTTP - if the exploit can fit into simple GET or POST commands.
If attackers can not attack the device vulnerability through the Internet directly, or via CSRF, but have connected to the same network - the network exposure shrinks significantly. And when attackers are on the same network as you, I bet you have bigger problems than the security of the IoT devices ...
Recommendations for home users
Don't buy **** you don't need
Disconnect from the power cord the IoT devices you don't need to operate 7*24.
Disconnect from the power cord the IoT devices you don't need to operate 7*24.
Disable cloud connectivity if it is not necessary. For example, I have a NAS device that can be reached through the "cloud", but I have disabled it by not configuring any default gateway for the device. I prefer connecting to my network via VPN and reach all my stuff through that.
Prevent CSRF attacks. I use two tricks. Don't use the 192.168.0.x - 192.168.10.x network at-home - use an uncommon IP range instead (e.g. 192.168.156.x is better). The second trick is I configured my Adblock plugin in my primary browser to block access to my internal network. And I use another browser whenever I want to access my internal devices. Update: On Firefox you can use NoScript ABE to block access to internal resources.
Check your router configuration:
- disable UPnP
- check the firewall settings and disable unnecessary port forwards
- check for IPv6 settings, and configure the firewall as default deny for incoming IPv6 TCP/UDP.
Change default passwords, especially for services connected to the Internet. Follow password best practices.
Run Nmap to locate new IoT in your home network :)
Run a WiFi scan to locate new WiFi access points. Let me share a personal experience with you. I moved to a new house and brought my own WiFi router with me. I plugged it in, and forget about WiFi. Months later it turned out I had two other WiFi devices in my house - the cable modem had its own integrated WiFi with default passwords printed on the bottom, and the Set-top-box was the same - default WiFi passwords printed on the bottom. And don't forget to scan for ZigBee, Bluetooth, IrDA, FM, ...
Update your devices - in case you have a lot of free time in your hand.
Don't allow your guests to connect to your home network. Set up a separated AP for them. Imagine your nephew stealing your private photos or videos from your NAS or DNLA server.
With great power, comes great responsibility. The less device you own in your house, the less time you need to maintain those.
Read the manuals of your devices. Be aware of the different interfaces. Configure it in a secure way.
Disable Teredo protocol in case you don't need IPv6.
Stop being amazed by junk hacking.
Update: Disable WebRTC: https://www.browserleaks.com/webrtc , in Chrome you can use this extension: https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/webrtc-network-limiter/npeicpdbkakmehahjeeohfdhnlpdklia
Update: Disable WebRTC: https://www.browserleaks.com/webrtc , in Chrome you can use this extension: https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/webrtc-network-limiter/npeicpdbkakmehahjeeohfdhnlpdklia
Update: Prevent against DNS rebind attacks via configuring a DNS server which can block internal IP addresses. OpenDNS can block internal IP, but this is not a default option, you have to configure it.
Recommendations for vendors
For vendors, I recommend at least the followings:
- Implement security during Software Development LifeCycle
- Continuous security testing and bug bounties
- Seamless auto-update
- Opt-in cloud connectivity
Recommendations for journalists
Stop FUD. Pretty please.
The questions to ask before losing your head
- who can exploit the vulnerability?
- what prerequisites do we have about the attack to successfully exploit the vulnerability? Is the attacker already in your home network? If yes, you have probably bigger problems.
- what can the attacker do when the exploit is successful?
And last but not least, don't forget that in the case of IoT devices, sometimes users are the product, not the customer. IoT is about collecting data for marketing purposes.
Related articles
- Pentest Web Application
- Hacking Bluetooth
- Hacker Types
- Hacking With Linux
- Pentest Android App
- Hacking Device
- Basic Pentest 1 Walkthrough
- Pentest Active Directory
- Hacking Jacket
- Pentest Ftp
- Hacking Wifi
- Pentest Bootcamp
- Hacker Google
- Pentest Reporting Tool
- Pentest Magazine
- Pentestmonkey Sql Injection
- Pentest Book
- Hacker Ethic
- Pentest Windows
- Pentest Basics
HiddenWasp Linux Malware Backdoor Samples
Here are Hidden Wasp Linux backdoor samples.
Enjoy
Reference

Intezer HiddenWasp Malware Stings Targeted Linux Systems
Download
File informatio
8914fd1cfade5059e626be90f18972ec963bbed75101c7fbf4a88a6da2bc671b
8f1c51c4963c0bad6cf04444feb411d7
shell
f321685342fa373c33eb9479176a086a1c56c90a1826a0aef3450809ffc01e5d
52137157fdf019145d7f524d1da884d7
elf
f38ab11c28e944536e00ca14954df5f4d08c1222811fef49baded5009bbbc9a2
ba02a964d08c2afe41963bf897d385e7
shell
e9e2e84ed423bfc8e82eb434cede5c9568ab44e7af410a85e5d5eb24b1e622e3
cbcda5c0dba07faced5f4641aab1e2cd
elf shared-lib
d66bbbccd19587e67632585d0ac944e34e4d5fa2b9f3bb3f900f517c7bbf518b
2b13e6f7d9fafd2eca809bba4b5ea9a6
64bits elf shared-lib
2ea291aeb0905c31716fe5e39ff111724a3c461e3029830d2bfa77c1b3656fc0
568d1ebd8b6fb17744d3c70837e801b9
shell
8e3b92e49447a67ed32b3afadbc24c51975ff22acbd0cf8090b078c0a4a7b53d
33c3f807caea64293add29719596f156
shell
609bbf4ccc2cb0fcbe0d5891eea7d97a05a0b29431c468bf3badd83fc4414578
71d78c97eb0735ec6152a6ff6725b9b2
tar-bundle gzip contains-elf
d596acc70426a16760a2b2cc78ca2cc65c5a23bb79316627c0b2e16489bf86c0
6d1cd68384de9839357a8be27894182b
tar-bundle gzip
0fe1248ecab199bee383cef69f2de77d33b269ad1664127b366a4e745b1199c8
5b134e0a1a89a6c85f13e08e82ea35c3
64bits elf
More information
Wednesday, June 10, 2020
How To Fetch Data From The Database | Tutorial 4
Welcome to my another PHP and MYSQL tutorial. In the previous I've discussed about the data insertion into database by using PHP and MYSQL. So i did successfully in the previous video.
In this video tutorial I'll discuss How to fetch data from the database called as data fetching. It's really a simple thing to access your data which is in database. You just have to do a little work for this. For fetching data you have follow some steps.
How to Fetch Data from Database
Step 1:
Make a connection with your database which i did in the previous blog.
Step 2:
If you wanna fetching a values in "form" or in a table so just have to create a form, table or whatever you want in HTML. I've created a table where I'll show you how to fetch data in table form.
Step 3:
Write a query SELECT * FROM table_Name;
Step 4:
Create a Loop for fetching all the data on a single click.
Step 5:
Create variables for the sake of storing a different values from the combined values in the loop variable like:
//while loop to fetch all the values from the database and stored in the variable named "row".
while($row = mysql_fetch_array(mysql_query($conn,$query))){
$name = $row['username']; //$name will save all the username values from the loop variable 'row'.
$pass = $row['password']; //$pass will save the password values from the loop variable 'row'.
}
Now watch the video for better understanding.
Related articles
- Hacker Keyboard
- Pentest Enumeration
- Pentest Uk
- Hacking To The Gate
- Pentest Usb
- Hacking Jacket
- Hacking Wifi
- Hacking Growth
- Hacking 3Ds
- Pentest Owasp Top 10
- Pentest Blog
- Pentest Documentation
- Hacking Youtube
- Pentesting And Ethical Hacking
- Pentest Usb
- Is Hacking Illegal
- Pentest+ Vs Ceh
- How To Pentest A Network
- Hacking Resources
- Hacking Programs
TERMINOLOGIES OF ETHICAL HACKING
What is the terminologies in ethical hacking?
Here are a few key terms that you will hear in discussion about hackers and what they do:
1-Backdoor-A secret pathway a hacker uses to gain entry to a computer system.
2-Adware-It is the softw-are designed to force pre-chosen ads to display on your system.
3-Attack-That action performs by a attacker on a system to gain unauthorized access.
4-Buffer Overflow-It is the process of attack where the hacker delivers malicious commands to a system by overrunning an application buffer.
5-Denial-of-Service attack (DOS)-A attack designed to cripple the victim's system by preventing it from handling its normal traffic,usally by flooding it with false traffic.
6-Email Warm-A virus-laden script or mini-program sent to an unsuspecting victim through a normal-looking email message.
7-Bruteforce Attack-It is an automated and simplest kind of method to gain access to a system or website. It tries different combination of usernames and passwords,again & again until it gets in from bruteforce dictionary.
8-Root Access-The highest level of access to a computer system,which can give them complete control over the system.
9-Root Kit-A set of tools used by an intruder to expand and disguise his control of the system.It is the stealthy type of software used for gain access to a computer system.
10-Session Hijacking- When a hacker is able to insert malicious data packets right into an actual data transmission over the internet connection.
11-Phreaker-Phreakers are considered the original computer hackers who break into the telephone network illegally, typically to make free longdistance phone calls or to tap lines.
12-Trojan Horse-It is a malicious program that tricks the computer user into opening it.There designed with an intention to destroy files,alter information,steal password or other information.
13-Virus-It is piece of code or malicious program which is capable of copying itself has a detrimental effect such as corrupting the system od destroying data. Antivirus is used to protect the system from viruses.
14-Worms-It is a self reflicating virus that does not alter files but resides in the active memory and duplicate itself.
15-Vulnerability-It is a weakness which allows a hacker to compromise the security of a computer or network system to gain unauthorized access.
16-Threat-A threat is a possible danger that can exploit an existing bug or vulnerability to comprise the security of a computer or network system. Threat is of two types-physical & non physical.
17-Cross-site Scripting-(XSS) It is a type of computer security vulnerability found in web application.It enables attacker to inject client side script into web pages viwed by other users.
18-Botnet-It is also known as Zombie Army is a group of computers controlled without their owner's knowledge.It is used to send spam or make denial of service attacks.
19-Bot- A bot is a program that automates an action so that it can be done repeatedly at a much higher rate for a period than a human operator could do it.Example-Sending HTTP, FTP oe Telnet at a higer rate or calling script to creat objects at a higher rate.
20-Firewall-It is a designed to keep unwanted intruder outside a computer system or network for safe communication b/w system and users on the inside of the firewall.
21-Spam-A spam is unsolicited email or junk email sent to a large numbers of receipients without their consent.
22-Zombie Drone-It is defined as a hi-jacked computer that is being used anonymously as a soldier or drone for malicious activity.ExDistributing Unwanted Spam Emails.
23-Logic Bomb-It is a type of virus upload in to a system that triggers a malicious action when certain conditions are met.The most common version is Time Bomb.
24-Shrink Wrap code-The process of attack for exploiting the holes in unpatched or poorly configured software.
25-Malware-It is an umbrella term used to refer a variety of intrusive software, including computer viruses,worms,Trojan Horses,Ransomeware,spyware,adware, scareware and other malicious program.
Follow me on instagram-anoymous_adi
- Hacker Anonymous
- Hacker Google
- Pentest Example Report
- Hackintosh
- How To Pentest A Website With Kali
- Hacking Games Online
- Pentest Tools Free
- Pentest Basics
- Pentest Web Application
- Pentesting And Ethical Hacking
- Hacking With Linux
- Pentest Online Course
- Hacking Quotes
- Hacking 3Ds
- Pentest With Kali
- Pentest Dns Server
- Pentest Vpn
- Pentest Lab Setup
- Hacker Forum
- Hacker Google
Hash Identifier - The Hash Identify Tool
Related posts
- Pentesting And Ethical Hacking
- Hacking Link
- Hacker Website
- Hacking The System
- Pentest As A Service
- Pentest Checklist
- Pentest Services
- Pentest Gear
- Pentest Magazine
- Pentest Magazine
- What Hacking Is
- Pentest Stages
- Pentest Gear
- Pentest Security
- Hacking Jailbreak
- Hacking Device
- Pentest Report Generator
- Pentest Services
- Hacking With Python
FOOTPRITING AND INFORMATION GATHERING USED IN HACKING
WHAT IS FOOTPRITING AND INFORMATION GATHERING IN HACKING?
Footpriting is the technique used for gathering information about computer systems and the entities they belongs too.
To get this information, a hacker might use various tools and technologies.
Basically it is the first step where hacker gather as much information as possible to find the way for cracking the whole system or target or atleast decide what types of attacks will be more suitable for the target.
Footpriting can be both passive and active.
Reviewing a company's website is an example of passive footprinting,
whereas attempting to gain access to sensititve information through social engineering is an example of active information gathering.
During this phase hacking, a hacker can collect the following information>- Domain name
-IP Addresses
-Namespaces
-Employee information
-Phone numbers
-E-mails
Job information
Tip-You can use http://www.whois.com/ website to get detailed information about a domain name information including its owner,its registrar, date of registration, expiry, name servers owner's contact information etc.
Use of Footprinting & Information Gathering in People Searching-
Now a days its very easy to find anyone with his/her full name in social media sites like Facebook, Instragram,Twitter,Linkdedin to gather information about date of birth,birthplace, real photos, education detail, hobbies, relationship status etc.
There are several sites like PIPL,PeekYou, Transport Sites such as mptransport,uptransport etc and Job placement Sites such as Shine.com,Naukari.com , Monster.com etc which are very useful for hacker to collect information about anyone.
Hacker collect the information about you from your Resume which you uploaded on job placement site for seeking a job as well as hacker collect the information from your vehicle number also from transport sites to know about the owner of vehicle, adderess etc then after they make plan how to attack on victim to earn money after know about him/her from collecting information.
INFORMATION GATHERING-It is the process of collecting the information from different places about any individual company,organization, server, ip address or person.
Most of the hacker spend his time in this process.
Information gathering plays a vital role for both investigating and attacking purposes.This is one of the best way to collect victim data and find the vulnerability and loopholes to get unauthorized modifications,deletion and unauthorized access.
Related articlesFootpriting is the technique used for gathering information about computer systems and the entities they belongs too.
To get this information, a hacker might use various tools and technologies.
Basically it is the first step where hacker gather as much information as possible to find the way for cracking the whole system or target or atleast decide what types of attacks will be more suitable for the target.
Footpriting can be both passive and active.
Reviewing a company's website is an example of passive footprinting,
whereas attempting to gain access to sensititve information through social engineering is an example of active information gathering.
During this phase hacking, a hacker can collect the following information>- Domain name
-IP Addresses
-Namespaces
-Employee information
-Phone numbers
-E-mails
Job information
Tip-You can use http://www.whois.com/ website to get detailed information about a domain name information including its owner,its registrar, date of registration, expiry, name servers owner's contact information etc.
Use of Footprinting & Information Gathering in People Searching-
Now a days its very easy to find anyone with his/her full name in social media sites like Facebook, Instragram,Twitter,Linkdedin to gather information about date of birth,birthplace, real photos, education detail, hobbies, relationship status etc.
There are several sites like PIPL,PeekYou, Transport Sites such as mptransport,uptransport etc and Job placement Sites such as Shine.com,Naukari.com , Monster.com etc which are very useful for hacker to collect information about anyone.
Hacker collect the information about you from your Resume which you uploaded on job placement site for seeking a job as well as hacker collect the information from your vehicle number also from transport sites to know about the owner of vehicle, adderess etc then after they make plan how to attack on victim to earn money after know about him/her from collecting information.
INFORMATION GATHERING-It is the process of collecting the information from different places about any individual company,organization, server, ip address or person.
Most of the hacker spend his time in this process.
Information gathering plays a vital role for both investigating and attacking purposes.This is one of the best way to collect victim data and find the vulnerability and loopholes to get unauthorized modifications,deletion and unauthorized access.
5 Free Online Courses To Learn Artificial Intelligence
We are living in the era of fourth industrial revolution(4IR), where Artificial intelligence has a significant role to play. This 4IR technology embedded within societies and even into the human body. From Computer enthusiasts to common people, everyone should be aware and learn this breakthrough technology.
We think about gigantic Robots from Transformers when we hear about Artificial Intelligence(AI) which is a fiction in the past but a fact today, capable of transforming the whole tech world. The field of AI consists of more than Robots such as personal assistants, self-driving cars, apprenticeship learning, behavior cloning and so on. To learn about this advanced technology, thanks to the online learning resources which offers great content to get started with artificial intelligence.
Here are the 5 free e-learning courses on Artificial Intelligence
1. UC Berkeley CS188 Intro to AI
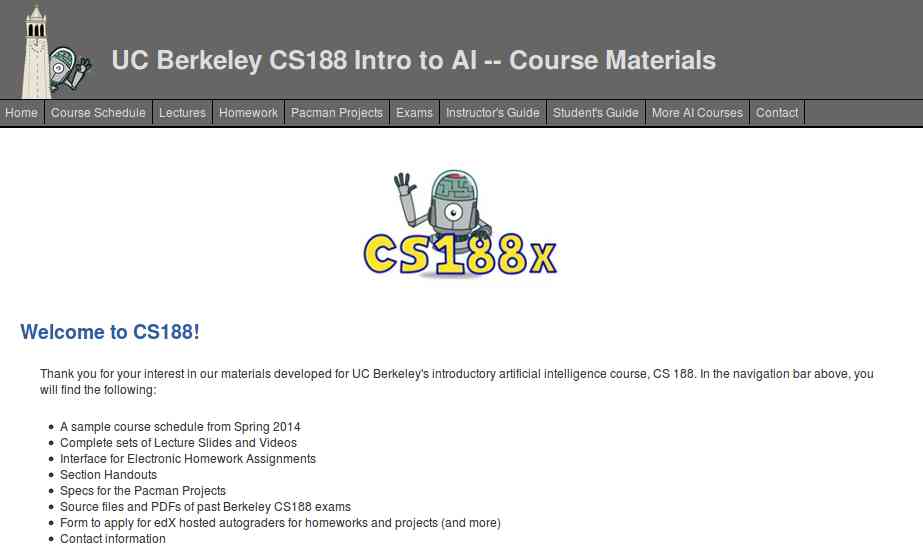
Get started with UC Berkeley AI course, this course is absolutely for beginners who are unaware of Artificial intelligence. It doesn't need any prior computer knowledge to know about AI. UC Berkeley allows anyone to learn this course for free. This course is systematically presented and consists of the following:
- Course Schedule
- Complete sets of Lecture Slides and Videos
- Interface for Electronic Homework Assignments
- Section Handouts
- Specs for the Pacman Projects
- Source files and PDFs of past Berkeley CS188 exams
- Form to apply for edX hosted autograders for homework and projects (and more)
- Contact information
Aside from this, you can also browse the following courses as well from UC Berkeley that are part of AI course:
- Machine Learning: CS189, Stat154
- Intro to Data Science: CS194-16
- Probability: EE126, Stat134
- Optimization: EE127
- Cognitive Modeling: CogSci131
- Machine Learning Theory: CS281A, CS281B
- Vision: CS280
- Robotics: CS287
- Natural Language Processing: CS288
2. Artificial Intelligence: Principles and Techniques
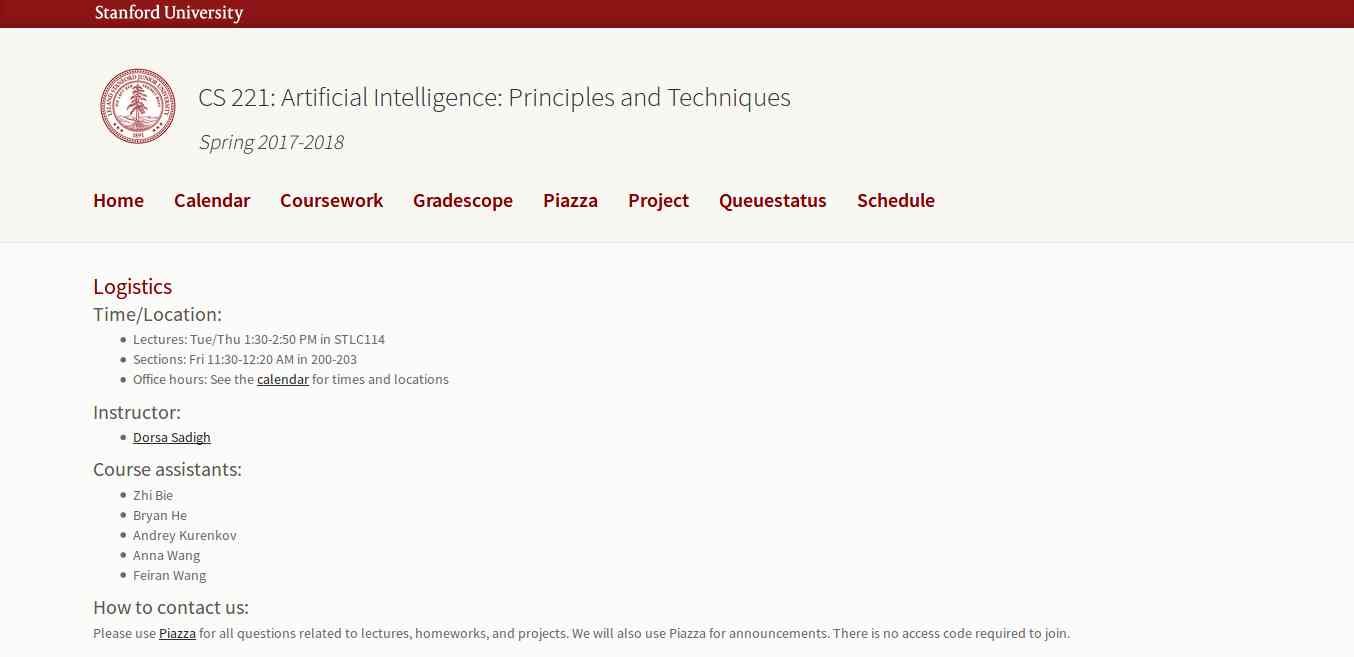
This course is offered by Stanford with great content that includes topics, videos, assignments, projects, and exams. The whole course mainly focuses on the complex real-world problems and try to find similarity between web search, speech recognition, face recognition, machine translation, autonomous driving, and automatic scheduling. Here you will learn the foundational principles of AI and implement some the AI systems. The goal of this course is to help you tackle the real-world situations with the help of AI tools. So, it is the best for the beginner to get started with AI.
3. Learn with GOOGLE AI
Who will dislike the course from Google? absolutely no one. This company is one of the early adopters of AI has a lot to offer to learners. Learn with Google AI is an education platform for people at all experience levels, it is free to access and browse content. The education resources provided by Google is from the machine learning experts of the company. These resources are the collections of lessons, tutorials, and Hands-on exercises that help you start learning, building, and problem-solving.
4. MIT 6.S094: Deep Learning for Self-Driving Cars
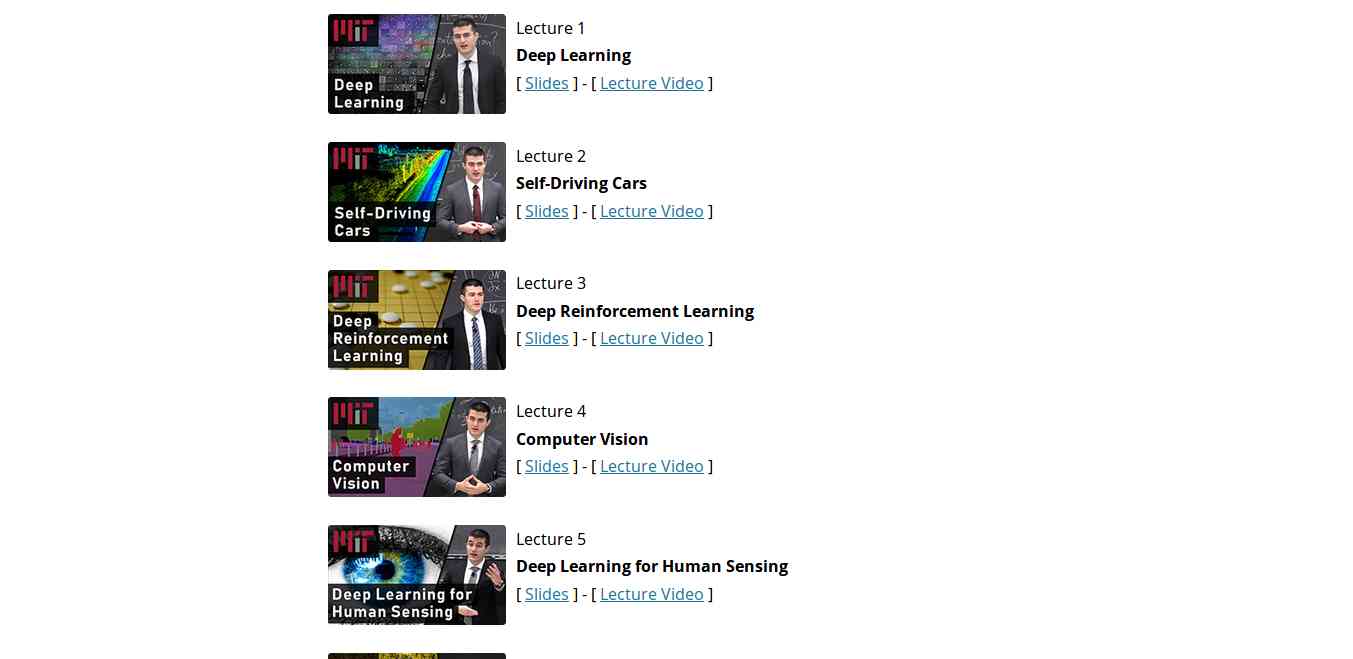
This course gives the practical overview of Deep Learning and AI. It is the course for beginners, also for the people who are getting started with Machine Learning. The course also offers a lot of benefits to the experienced and advanced researchers in the field deep learning. This MIT's course takes people into the journey of Deep Learning with the applied theme of building Self-Driving cars. However, the course also offers slides and videos to engage the learners.
5. Fundamentals of Deep Learning for Computer Vision
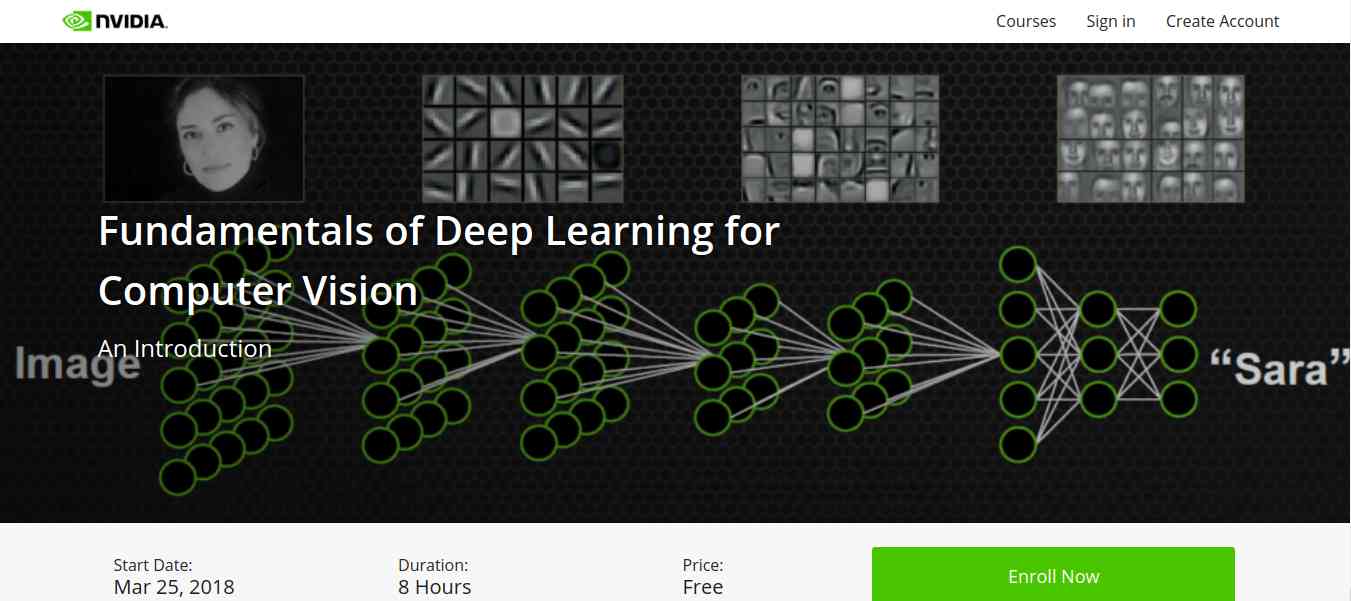
This course is offered by Nvidia and Nvidia Deep learning Institute. Computer Vision is one of the disciplines of AI that acquire, analyze, process, and understand images. The course is completely free and everyone who is enthusiast about AI can access and learn the course. It is a hands-on course that able to provide basics of deep learning and deployment of neural networks. With this. you will also learn the following:
- Identify the ingredients required to start a Deep Learning project.
- Train a deep neural network to correctly classify images it has never seen before.
- Deploy deep neural networks into applications.
- Identify techniques for improving the performance of deep learning applications.
- Assess the types of problems that are candidates for deep learning.
- Modify neural networks to change their behavior.
More info
S2 Dynamic Tracer And Decompiler For Gdb
Decompiling is very useful for understanding srtipped binaries, most dissasemblers like IDA or Hopper have a plugin for decompiling binaries, generating a c like pseudocode.
Static analysis, is very useful in most of cases, specially when the binary is not so big, or when you just have an address where to start to analyze. But some algorithms will be learned in less time by dynamic analysis like tracing or debugging.
In cookiemonsters team, we are working on several tracers with different focus, but all of them mix the concept of tracing and decompiling to generate human-readable traces.
S2 is my tracer & decompiler plugin for gdb, very useful for ctfs.
Some of the features are:
- signed/unsigned detecion
- conditional pseudocode (if)
- syscall resolution
- unroll bucles
- used registers values
- mem states
- strings
- logging
More articles
Tuesday, June 9, 2020
PHASES OF HACKING
What is the process of hacking or phases of hacking?
Hacking is broken up into six phases:The more you get close to all phases,the more stealth will be your attack.
1-Reconnaissance-This is the primary phase of hacking where hacker tries to collect as much as information as possible about the target.It includes identifying the target,domain name registration records of the target, mail server records,DNS records.The tools that are widely used in the process is NMAP,Hping,Maltego, and Google Dorks.
2-Scanning-This makes up the base of hacking! This is where planning for attack actually begins! The tools used in this process are Nessus,Nexpose,and NMAP. After reconnaissance the attacker scans the target for services running,open ports,firewall detection,finding out vulnerabilities,operating system detection.
3-Gaining Access-In this process the attacker executes the attack based on vulnerabilities which were identified during scanning! After the successful, he get access to the target network or enter in to the system.The primary tools that is used in this process is Metasploit.
4-Maintaining Access-It is the process where the hacker has already gained access in to a system. After gaining access the hacker, the hacker installs some backdoors in order to enter in to the system when he needs access in this owned system in future. Metasploit is the preffered toll in this process.
5-Clearning track or Covering track-To avoid getting traced and caught,hacker clears all the tracks by clearing all kinds of logs and deleted the uploaded backdoor and anything in this process related stuff which may later reflect his presence!
6-Reporting-Reporting is the last step of finishing the ethical hacking process.Here the Ethical Hacker compiles a report with his findings and the job that was done such as the tools used,the success rate,vulnerabilities found,and the exploit process.
Related articlesHacking is broken up into six phases:The more you get close to all phases,the more stealth will be your attack.
1-Reconnaissance-This is the primary phase of hacking where hacker tries to collect as much as information as possible about the target.It includes identifying the target,domain name registration records of the target, mail server records,DNS records.The tools that are widely used in the process is NMAP,Hping,Maltego, and Google Dorks.
2-Scanning-This makes up the base of hacking! This is where planning for attack actually begins! The tools used in this process are Nessus,Nexpose,and NMAP. After reconnaissance the attacker scans the target for services running,open ports,firewall detection,finding out vulnerabilities,operating system detection.
3-Gaining Access-In this process the attacker executes the attack based on vulnerabilities which were identified during scanning! After the successful, he get access to the target network or enter in to the system.The primary tools that is used in this process is Metasploit.
4-Maintaining Access-It is the process where the hacker has already gained access in to a system. After gaining access the hacker, the hacker installs some backdoors in order to enter in to the system when he needs access in this owned system in future. Metasploit is the preffered toll in this process.
5-Clearning track or Covering track-To avoid getting traced and caught,hacker clears all the tracks by clearing all kinds of logs and deleted the uploaded backdoor and anything in this process related stuff which may later reflect his presence!
6-Reporting-Reporting is the last step of finishing the ethical hacking process.Here the Ethical Hacker compiles a report with his findings and the job that was done such as the tools used,the success rate,vulnerabilities found,and the exploit process.
- Pentestbox
- How To Pentest A Website With Kali
- Pentest Tools
- Pentest Dns
- Pentest Tools
- Hackintosh
- What Hacking Is
- Pentest Azure
- Hacker News
- Pentest Ftp
- Hacking To The Gate
- Hacking With Python
- Hacker Wifi Password
- Hacking Tutorials
- Pentest+ Vs Ceh
- Hacker Attack
- Pentesting And Ethical Hacking
- Hacking Bluetooth
- Pentest +
Group Instant Messaging: Why Blaming Developers Is Not Fair But Enhancing The Protocols Would Be Appropriate
After presenting our work at Real World Crypto 2018 [1] and seeing the enormous press coverage, we want to get two things straight: 1. Most described weaknesses are only exploitable by the malicious server or by knowing a large secret number and thereby the protocols are still very secure (what we wrote in the paper but some newspapers did not adopt) and 2. we see ways to enhance the WhatsApp protocol without breaking its features.
We are of course very happy that our research reached so many people and even though IT security and cryptography are often hard to understand for outsiders, Andy Greenberg [2], Patrick Beuth [3] and other journalists [4,5,6,7,8] wrote articles that were understandable on the one hand and very accurate and precise on the other hand. In contrast to this, we also saw some inaccurate articles [9,10] that fanned fear and greatly diverged in their description from what we wrote in our paper. We expected this from the boulevard press in Germany and therefore asked them to stick to the facts when they were contacting us. But none of the worst two articles' [9,10] authors contacted us in advance. Since our aim was never to blame any application or protocol but rather we wanted to encourage the developers to enhance the protocols, it contradicts our aim that WhatsApp and Signal are partially declared attackable by "anyone" "easily" [9,10].
Against this background, we understand Moxie's vexation about certain headlines that were on the Internet in the last days [11]. However, we believe that the ones who understand the weaknesses, comprehend that only the malicious server can detectably make use of them (in WhatsApp) or the secret group ID needs to be obtained from a member (in Signal). As such, we want to make clear that our paper does not primarily focus on the description of weaknesses but presents a new approach for analyzing and evaluating the security of group instant messaging protocols. Further we propose measures to enhance the analyzed protocols. The description of the protocols' weaknesses is only one part of the evaluation of our analysis approach and thereby of the investigation of real world protocols. This is the scientific contribution of our paper. The practical contribution of the analyzed messengers, which is the communication confidentiality for billion users (in most cases), is great and should be noted. Therefore we believe that being Signal, WhatsApp, or Threema by applying encryption to all messages and consequently risking research with negative results is much better than being a messenger that does not encrypt group messages end-to-end at all. We do not want to blame messengers that are far less secure (read Moxie's post [11] if you are interested).
Finally we want note that applying security measures according to the ticket approach (as we call it in the paper [12]) to the invitation links would solve the issues that Facebook's security head mentioned in his reply [13] on our findings. To our knowledge, adding authenticity to group update messages would not affect invitation links: If no invitation link was generated for a group, group members should only accept joining users if they were added by an authentic group update message. As soon as a group invitation link was generated, all joining users would need to be accepted as new group members with the current design. However there are plenty ways how WhatsApp could use invitation links without endowing the server with the power to manage groups without the group admins' permission:
One approach would be generating the invitation links secretly and sharing them without the knowledge of the server. An invitation link could then contain a secret ticket for the group and the ID of the group. As soon as a user, who received the link, wants to join the group, she can request the server with the group ID to obtain all current group members. The secret ticket can now be sent to all existing group members encrypted such that the legitimate join can be verified.
Of course this would require engineering but the capability of WhatsApp, shipping drastic protocol updates, can be assumed since they applied end-to-end encryption in the first place.
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i5i38WlHfds
[2] https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-security-flaws-encryption-group-chats/
[3] http://www.spiegel.de/netzwelt/apps/whatsapp-gruppenchats-schwachstelle-im-verschluesselungs-protokoll-a-1187338.html
[4] http://www.sueddeutsche.de/digital/it-sicherheit-wie-fremde-sich-in-whatsapp-gruppenchats-einladen-koennen-1.3821656
[5] https://techcrunch.com/2018/01/10/security-researchers-flag-invite-bug-in-whatsapp-group-chats/
[6] http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/2018/01/10/whatsapp-bug-raises-questions-group-message-privacy/
[7] http://www.handelsblatt.com/technik/it-internet/verschluesselung-umgangen-forscher-finden-sicherheitsluecke-bei-whatsapp/20836518.html
[8] https://www.heise.de/security/meldung/WhatsApp-und-Signal-Forscher-beschreiben-Schwaechen-verschluesselter-Gruppenchats-3942046.html
[9] https://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/3024215/whatsapp-bug-lets-anyone-easily-infiltrate-private-group-chats
[10] http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-5257713/WhatsApp-security-flaw-lets-spy-private-chats.html
[11] https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=16117487
[12] https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/713.pdf
[13] https://twitter.com/alexstamos/status/951169036947107840
Further articles:
- Matthew Green's blog post: https://blog.cryptographyengineering.com/2018/01/10/attack-of-the-week-group-messaging-in-whatsapp-and-signal/
- Schneier on Security: https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2018/01/whatsapp_vulner.html
- Bild: http://www.bild.de/digital/smartphone-und-tablet/whatsapp/whatsapp-sicherheitsluecke-in-gruppenchats-54452080.bild.html
- Sun: https://www.thesun.co.uk/tech/5316110/new-whatsapp-bug-how-to-stay-safe/
We are of course very happy that our research reached so many people and even though IT security and cryptography are often hard to understand for outsiders, Andy Greenberg [2], Patrick Beuth [3] and other journalists [4,5,6,7,8] wrote articles that were understandable on the one hand and very accurate and precise on the other hand. In contrast to this, we also saw some inaccurate articles [9,10] that fanned fear and greatly diverged in their description from what we wrote in our paper. We expected this from the boulevard press in Germany and therefore asked them to stick to the facts when they were contacting us. But none of the worst two articles' [9,10] authors contacted us in advance. Since our aim was never to blame any application or protocol but rather we wanted to encourage the developers to enhance the protocols, it contradicts our aim that WhatsApp and Signal are partially declared attackable by "anyone" "easily" [9,10].
Against this background, we understand Moxie's vexation about certain headlines that were on the Internet in the last days [11]. However, we believe that the ones who understand the weaknesses, comprehend that only the malicious server can detectably make use of them (in WhatsApp) or the secret group ID needs to be obtained from a member (in Signal). As such, we want to make clear that our paper does not primarily focus on the description of weaknesses but presents a new approach for analyzing and evaluating the security of group instant messaging protocols. Further we propose measures to enhance the analyzed protocols. The description of the protocols' weaknesses is only one part of the evaluation of our analysis approach and thereby of the investigation of real world protocols. This is the scientific contribution of our paper. The practical contribution of the analyzed messengers, which is the communication confidentiality for billion users (in most cases), is great and should be noted. Therefore we believe that being Signal, WhatsApp, or Threema by applying encryption to all messages and consequently risking research with negative results is much better than being a messenger that does not encrypt group messages end-to-end at all. We do not want to blame messengers that are far less secure (read Moxie's post [11] if you are interested).
Finally we want note that applying security measures according to the ticket approach (as we call it in the paper [12]) to the invitation links would solve the issues that Facebook's security head mentioned in his reply [13] on our findings. To our knowledge, adding authenticity to group update messages would not affect invitation links: If no invitation link was generated for a group, group members should only accept joining users if they were added by an authentic group update message. As soon as a group invitation link was generated, all joining users would need to be accepted as new group members with the current design. However there are plenty ways how WhatsApp could use invitation links without endowing the server with the power to manage groups without the group admins' permission:
One approach would be generating the invitation links secretly and sharing them without the knowledge of the server. An invitation link could then contain a secret ticket for the group and the ID of the group. As soon as a user, who received the link, wants to join the group, she can request the server with the group ID to obtain all current group members. The secret ticket can now be sent to all existing group members encrypted such that the legitimate join can be verified.
Of course this would require engineering but the capability of WhatsApp, shipping drastic protocol updates, can be assumed since they applied end-to-end encryption in the first place.
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i5i38WlHfds
[2] https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-security-flaws-encryption-group-chats/
[3] http://www.spiegel.de/netzwelt/apps/whatsapp-gruppenchats-schwachstelle-im-verschluesselungs-protokoll-a-1187338.html
[4] http://www.sueddeutsche.de/digital/it-sicherheit-wie-fremde-sich-in-whatsapp-gruppenchats-einladen-koennen-1.3821656
[5] https://techcrunch.com/2018/01/10/security-researchers-flag-invite-bug-in-whatsapp-group-chats/
[6] http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/2018/01/10/whatsapp-bug-raises-questions-group-message-privacy/
[7] http://www.handelsblatt.com/technik/it-internet/verschluesselung-umgangen-forscher-finden-sicherheitsluecke-bei-whatsapp/20836518.html
[8] https://www.heise.de/security/meldung/WhatsApp-und-Signal-Forscher-beschreiben-Schwaechen-verschluesselter-Gruppenchats-3942046.html
[9] https://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/3024215/whatsapp-bug-lets-anyone-easily-infiltrate-private-group-chats
[10] http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-5257713/WhatsApp-security-flaw-lets-spy-private-chats.html
[11] https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=16117487
[12] https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/713.pdf
[13] https://twitter.com/alexstamos/status/951169036947107840
Further articles:
- Matthew Green's blog post: https://blog.cryptographyengineering.com/2018/01/10/attack-of-the-week-group-messaging-in-whatsapp-and-signal/
- Schneier on Security: https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2018/01/whatsapp_vulner.html
- Bild: http://www.bild.de/digital/smartphone-und-tablet/whatsapp/whatsapp-sicherheitsluecke-in-gruppenchats-54452080.bild.html
- Sun: https://www.thesun.co.uk/tech/5316110/new-whatsapp-bug-how-to-stay-safe/
More information
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)










